Level 1: SQL Exploration
Objective: Find and understand your dataset.
Story beat Before you analyze anything, you must locate who in the dataset lives in RJ and what orders belong to them. You’re drawing a map of the crisis zone.
Problem 1.1: Know Your Audience (Simple Filtering)
Business Value: Before we analyze behavior, we need to know the size of our cohort in Rio de Janeiro.
-
Goal: List all customer profiles located in the state of Rio de Janeiro ('RJ').
-
Success Criteria:
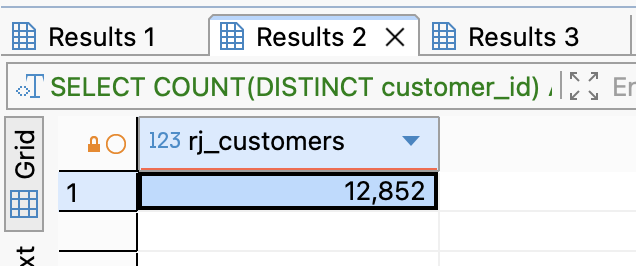
- "How many unique customers do we have in Rio de Janeiro?" (Hint: It should be around 12,000+ rows).
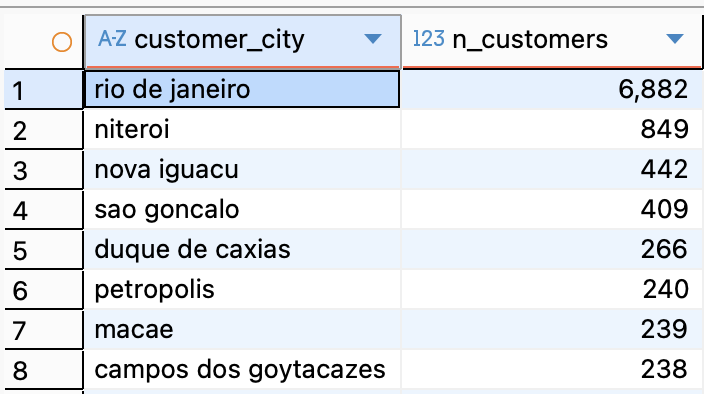
- "Besides the city 'rio de janeiro', what other cities appear in this list?"
💡 Hint
- Which table contains customer location information?
- What column would tell you the state where a customer lives?
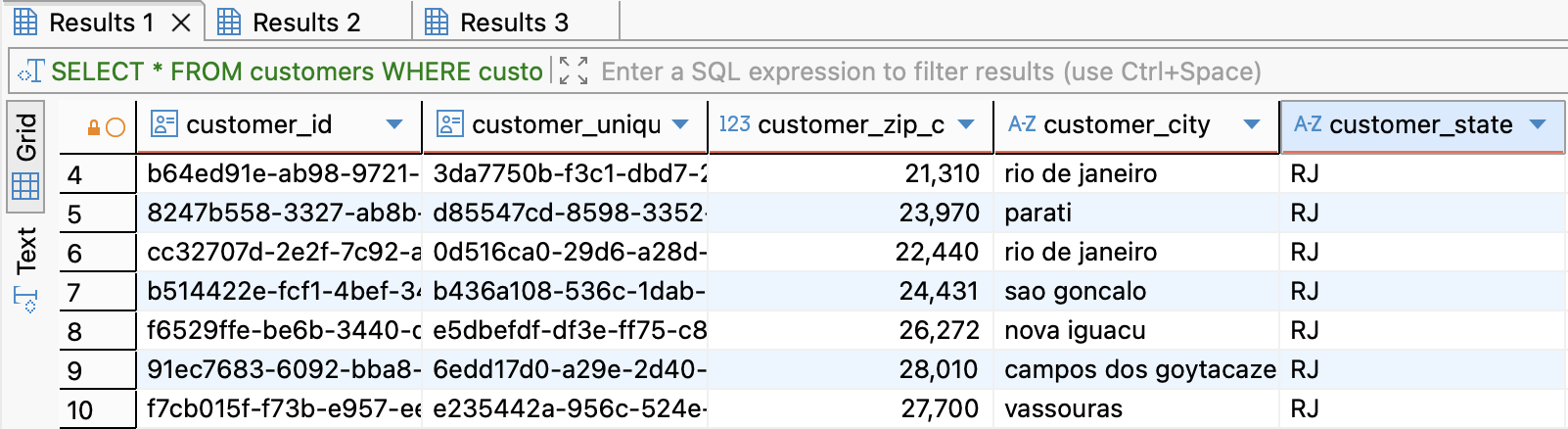
- Question 1: List all customer profiles located in the state of Rio de Janeiro ('RJ')
SELECT *
FROM customers
WHERE customer_state = 'RJ';
- Question 2: How many unique customers do we have in Rio de Janeiro?
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT customer_id) AS rj_customers
FROM customers
WHERE customer_state = 'RJ';
- Question 3: Besides the city 'rio de janeiro', what other cities appear in this list?
SELECT
customer_city,
COUNT(DISTINCT customer_id) AS n_customers
FROM customers
WHERE customer_state = 'RJ'
GROUP BY customer_city
ORDER BY n_customers DESC, customer_city;
Problem 1.2: The Transaction History (Basic Join)
Business Value: A customer profile is useless without their purchase history. We need to attach orders to these people.
-
Goal: Join the Orders table to the Customers table to find every order placed by an RJ customer.
-
Success Criteria:
- "Does the row count match your previous query, or is it different? Why?"
- "Can you see the
order_statuscolumn in the results?"
💡 Hint
- You need to combine customer and order information
- What field connects customers to their orders?
- Build upon your previous query from Problem 1
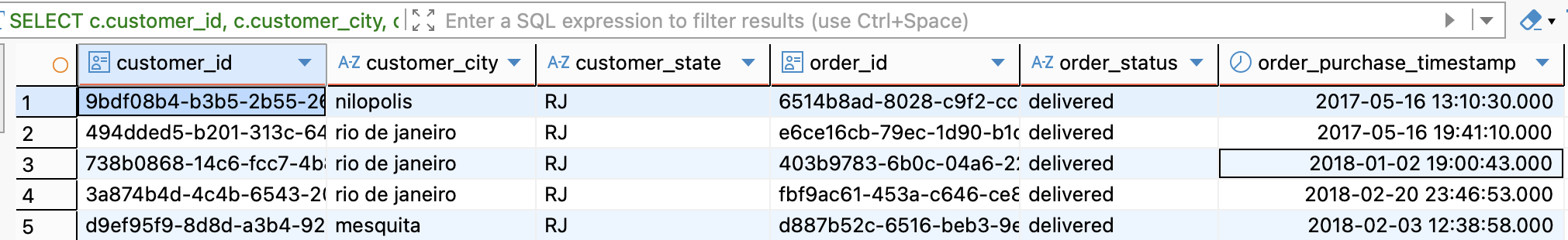
-Question 1: Join the Orders table to the Customers table to find every order placed by an RJ customer:
SELECT
c.customer_id,
c.customer_city,
c.customer_state,
o.order_id,
o.order_status,
o.order_purchase_timestamp
FROM customers c
JOIN orders o
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
WHERE c.customer_state = 'RJ';
-
Question 2:Does the row count match your previous query, or is it different? Why?
Số lượng row khác nhau giữa problem 1.2 và problem 1.1( ở 1.2 lớn hơn) do ở 1.1 lấy kết quả theo unique customers, tức mỗi hàng tương ứng với 1 KH; còn problem 1.2 lấy tất cả các đơn hàng của KH sống ở bang RJ, 1 dòng tương ứng với 1 đơn hàng do đó 1 KH có thể có nhiều đơn hàng => số rows nhiều hơn problem 1.1
-
Question 3:"Can you see the order_status column in the results?"
Cột order_status xuất hiện vì sau khi join bảng Orders với bảng Customers, tất cả thông tin đơn hàng liên quan đến mỗi khách hàng ở RJ đều được đưa vào kết quả.
Problem 1.3: The Timeline (Date Handling)
Business Value: The VP needs to know if this is a recent problem or a historical one. We need to establish the date range of our data.
-
Goal: Find the date range of all orders placed in RJ.
-
Success Criteria:
- "What is the date of the very first order in RJ?"
- "When was the last order placed?"
- "Does this cover the Black Friday period?"
💡 Hint
- Think about aggregate functions for finding earliest and latest values
- Which column contains the purchase date/time?
- Consider formatting the output for better readability
- Question 1: “What is the date of the very first order in RJ?” Hướng giải quyết
- JOIN bảng orders với customers dựa trên customer_id
- Chỉ giữ khách có customer_state = 'RJ'
- Lấy giá trị nhỏ nhất (MIN) của order_purchase_timestamp
SELECT
DATE(MIN(o.order_purchase_timestamp)) AS first_order_date
FROM customers c
JOIN orders o
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
WHERE c.customer_state = 'RJ';
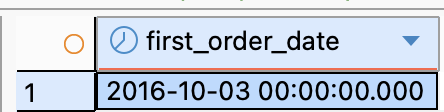
- Question 2: “When was the last order placed?” Hướng giải quyết
- JOIN như câu trên
- Lấy giá trị lớn nhất (MAX) của order_purchase_timestamp
SELECT
DATE(MAX(o.order_purchase_timestamp)) AS last_order_date
FROM customers c
JOIN orders o
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
WHERE c.customer_state = 'RJ';
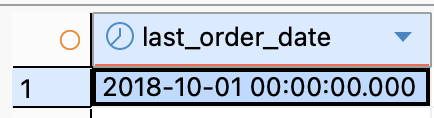
-
Question 3: "Does this cover the Black Friday period?"
Có, khoảng thời gian này bao gồm Black Friday của năm 2016 và 2017
-
**
Problem 1.4: The Funnel Audit (Aggregation & Nulls)
Business Value: Not all orders make it to the customer. We need to see how many orders were actually delivered vs. cancelled or unavailable.
-
Goal: Count the number of orders per
order_statusfor RJ customers. -
Success Criteria:
- "How many orders in RJ were 'canceled'?"
- "How many were 'delivered'?"
- Critical Check: "Are there any statuses where the count is surprisingly high?"
💡 Hint
- You need to count orders grouped by their status
- What SQL clause helps you organize data into categories?
- How can you sort the results to see the most common statuses first?
- Question 1: “How many orders in RJ were canceled?” Hướng giải quyết:
- JOIN customers (c) với orders (o) qua customer_id
- Lọc khách hàng ở bang RJ: customer_state = 'RJ'
- Lọc thêm trạng thái đơn hàng: order_status = 'canceled'
SELECT
COUNT(*) AS canceled_orders_in_RJ
FROM customers c
JOIN orders o
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
WHERE c.customer_state = 'RJ'
AND o.order_status = 'canceled';

- Question 2: “How many were delivered?” Hướng giải quyết:
- JOIN customers (c) với orders (o) qua customer_id
- Thay điều kiện trạng thái thành order_status = 'delivered'
SELECT
COUNT(*) AS delivered_orders_in_RJ
FROM customers c
JOIN orders o
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
WHERE c.customer_state = 'RJ'
AND o.order_status = 'delivered';

- Question 3: “Are there any statuses where the count is surprisingly high?” Hướng giải quyết:
- JOIN bảng customers(c) với orders(o) bằng customer_id
- Lọc khách sống ở RJ: customer_state = 'RJ'
- Group theo order_status.
- Sắp xếp giảm dần để xem trạng thái nào bất thường (quá cao hoặc quá thấp).
SELECT
o.order_status,
COUNT(*) AS order_count
FROM customers c
JOIN orders o
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
WHERE c.customer_state = 'RJ'
GROUP BY o.order_status
ORDER BY order_count DESC;
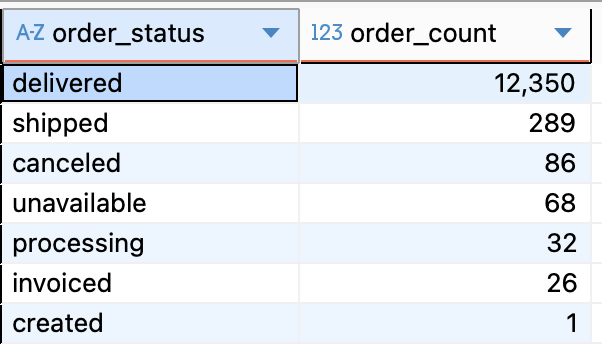
Problem 1.5: The "Pulse Check" (3-Table Join)
Business Value: Now we need the "Voice of the Customer." We need to see the average star rating for these specific orders.
-
Goal: Calculate the average review score for all delivered orders in RJ.
-
Success Criteria:
- "What is the average score for RJ? (Is it below 4.0?)"
- "How does this compare if you remove the 'RJ' filter and look at the whole country?"
💡 Hint
- You need to bring in review data from another table
- What aggregate function calculates averages?
- Remember to filter for both RJ customers and delivered orders only
- Question 1: "What is the average score for RJ? (Is it below 4.0?)" Hướng giải quyết:
- Cần JOIN 3 bảng: 1.customers → để lọc khách ở RJ 2.orders → để chỉ lấy đơn có order_status = 'delivered' 3.order_reviews → để lấy review_score
- JOIN qua khóa:
- customers.customer_id = orders.customer_id
- orders.order_id = order_reviews.order_id
- Lấy trung bình điểm review: AVG(review_score)
SELECT
AVG(r.review_score) AS avg_review_score_RJ
FROM customers c
JOIN orders o
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
JOIN order_reviews r
ON o.order_id = r.order_id
WHERE c.customer_state = 'RJ'
AND o.order_status = 'delivered';

- Question 2: “How does this compare if you remove the 'RJ' filter and look at the whole country?”
SELECT
AVG(r.review_score) AS avg_review_score_brazil
FROM orders o
JOIN order_reviews r
ON o.order_id = r.order_id
WHERE o.order_status = 'delivered';
